Aquatic ecosystems: Lakes and Ponds
Freshwater ecosystems cover 0.80% of the Earth's surface and inhabit 0.009% of its total water. They generate nearly 3% of its net primary production. Freshwater ecosystems contain 41% of the world's known fish species. Ponds are small pools with shallow water, marsh, and aquatic plants. There is usually a diverse array of aquatic life, with a few examples including
algae, snails, fish, beetles, water bugs, frogs, turtles, otters and muskrats. Top predators may include large fish, herons, or alligators. Since fish are a major predator upon amphibian larvae, ponds that dry up each year, thereby killing resident fish, provide important refugia for amphibian breeding. The ecosystem of a lake includes biotic (living) plants, animals and
micro-organisms, as well as abiotic(nonliving) physical and chemical interactions. Lake ecosystems are a prime examples of lentic ecosystems.
algae, snails, fish, beetles, water bugs, frogs, turtles, otters and muskrats. Top predators may include large fish, herons, or alligators. Since fish are a major predator upon amphibian larvae, ponds that dry up each year, thereby killing resident fish, provide important refugia for amphibian breeding. The ecosystem of a lake includes biotic (living) plants, animals and
micro-organisms, as well as abiotic(nonliving) physical and chemical interactions. Lake ecosystems are a prime examples of lentic ecosystems.
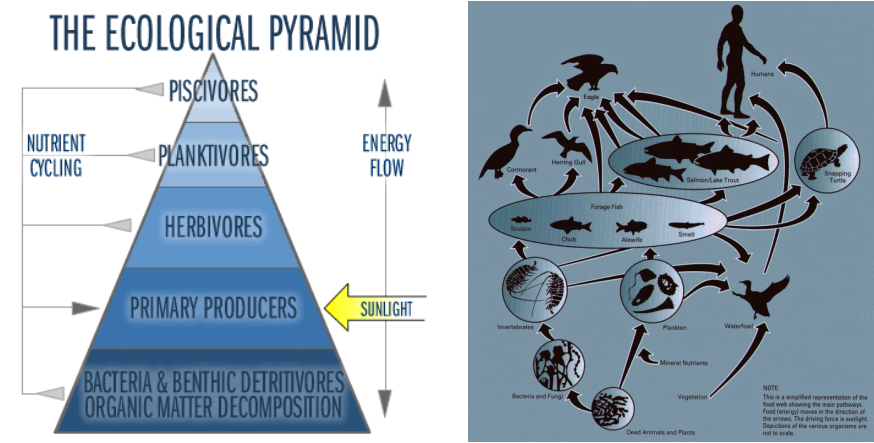
The pictures above show the energy and food flow throughout the organisms that live in a lake. To the right, you'll see that eagles and humans are top consumers, while bacteria, fungi and vegetation are the top producers.